2.2 Method of Short Cavity
According to the theoretical analysis of E-O Q-switching, when the laser crystal, pump power, oscillating laser beam diameter and repetition frequency are determined, the shorter the cavity length, the narrower the pulse width. In order to obtain laser output with narrow pulse width, we can reduce the size of the optical elements in the cavity or use the voltage-decreased E-O Q-switching technique.
In 2010, a research team obtained a miniaturized laser with high efficiency, narrow pulse width and compact structure by using LD end-pumped Nd:YVO4 crystal with 10° wedge angle and LGS crystal as the E-O Q-switching element. The gain medium adopts the Nd:YVO4 crystal with wedge angle instead of the polarizer, which has the advantages of simplifying the components in the cavity, shortening the cavity length and reducing the loss. Such design is beneficial to improve the conversion efficiency and the performance of the narrow pulse width laser output. Finally, a laser output with repetition frequency of 1 kHz, single pulse energy of 2.2 mJ and pulse width of 6.3 ns was obtained.
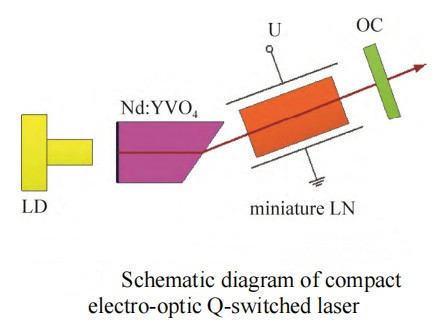
In 2018, someone developed a high repetition frequency short cavity laser system with narrow pulse width based on LN E-O Q-switching. The laser gain medium is Nd:YVO4 crystal with large stimulated emission cross section and short fluorescence life. The pump end of the laser crystal is coated with high reflection film at 1064 nm instead of a rear mirror, and the other end is cut along the Bluster angle instead of a polarizer to shorten the cavity length. The voltage-decreased E-O Q-switching method is adopted to eliminate the quarter waveplate and further shorten the cavity length. The length of the designed resonator is only 20 mm, and the maximum repetition rate is 15 kHz, the single pulse energy is 238 μJ, and the pulse width is 5.4 ns. This compact E-O Q-switched laser design is shown below.
To use E-O Q-switching short cavity method to obtain narrow pulse width laser output, the following strategies are usually adopted: coating on one end of the gain medium instead of using a cavity mirror, cutting the other end with Bluster angle instead of using a polarizer, using the voltage-decreased E-O Q-switching method to eliminate the quarter waveplate. Compared with Pockels cell Q-switching method, the E-O deflector Q-switching approach can realize Q-switching without adding any other cavity elements except the deflector, which effectively compress the cavity length, reduce the insertion loss, and obtain the narrow pulse width laser output easily.
In 2016, people successfully used LD continuously end-pumped Nd:YVO4 laser crystal and RTP E-O deflector (with four-electrode structure) as Q-switch to make narrow pulse width laser output with repetition rate 5 kHz, single pulse energy 244 μJ, and pulse width 1.0 ns. At repetition rate of 20 kHz, the single pulse energy is 134 μJ and the pulse width is 2.2 ns. Compared with Pockels cell, E-O deflector Q-switching can make the laser structure more compact while obtain laser output with high repetition rate and narrow pulse width.
Post time: Nov-24-2022